Page 232 - DEDU403_EDUCATIONAL_TECHNOLOGY_ENGLISH
P. 232
Educational Technology
Notes
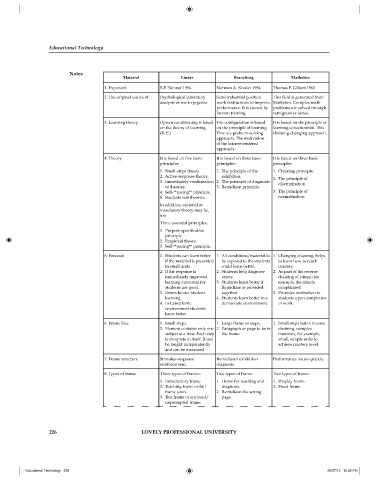
Material Linear Branching Mathetics
1. Exponent B.F. Skinner 1954 Normen A. Kroder 1954 Thomas F. Gilbert 1962
2. The original source of Psychological laboratory Semi-industrial position This field is generated from
analysis or use in pigeons. work instructions to improve Mathetics. Complex math
performance. It is caused by problems are solved through
human training. retrogressive series.
3. Learning theory Oprent conditioning is based The confi guration is based It is based on the principle of
on the theory of learning. on the principle of learning. learning conectionnist. This
(R. S.) This is a problem-solving chaining-changing approach.
approach. The motivation
of the learner-centered
approach.
4. Theory It is based on fi ve basic It is based on three basic It is based on three basic
principles: principles: principles:
1. Small-steps theory. 1. The principle of the 1. Chaining principle.
2. Active-response theory. exhibition. 2. The principle of
3. Immediately-confi rmation 2. The principle of diagnosis. discrimination.
of theories. 3. Remidiasn principle.
4. Self-**pacing** principle. 3. The principle of
5. Students test theories. normalization.
In addition, optional or
mandatory theory may be,
too.
Three essential principles:
1. Purpose specifi cation
principle.
2. Empirical theory.
3. Self-**pacing** principle.
5. Forecast 1. Students can learn better 1. All conditions/material to 1. Changing chaining, helps
if the material is presented be exposed to the students to learn how to reach
in small units. could learn better. mastery.
2. If the response is 2. Students help diagnose 2. As part of the reverse
immediately improved errors. chaining of stimuli for
learning outcomes for 3. Students learn better if example, the simple
students are good. Remidiasn is provided complicated.
3. Errors hinder student together. 3. Provides motivation to
learning. 4. Students learn better in a students upon completion
4. In Laisej ferric democratic environment. of work.
environment students
learn better.
6. Frame Size 1. Small steps. 1. Large frame or steps. 1. Small steps but in reverse
2. Element contains only one 2. Paragraph or page to be in chaining, complex
subject at a time. Each step the frame. materials, for example,
is complete in itself. It can small, simple units to
be taught independently achieve mastery level.
and can be measured.
7. Frame structure Stimulus-response Remidiasen exhibition Performance issues quickly.
reinforcement. diagnosis.
8. Types of frame Three types of frames: Two types of frame: Two types of frame:
1. Introductory frame 1. Home for teaching and 1. Display frame.
2. Teaching frame or full diagnosis. 2. Fixed frame
frame soon. 2. Remidiasn the wrong
3. Test frame or enclosed/ page.
unprompted frame.
226 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY
29/07/13 10:22 PM
Educational Technology 226 29/07/13 10:22 PM
Educational Technology 226