Page 300 - DCOM201_ACCOUNTING_FOR_COMPANIES_I
P. 300
Unit 12: Divisible Profits and Managerial Remuneration
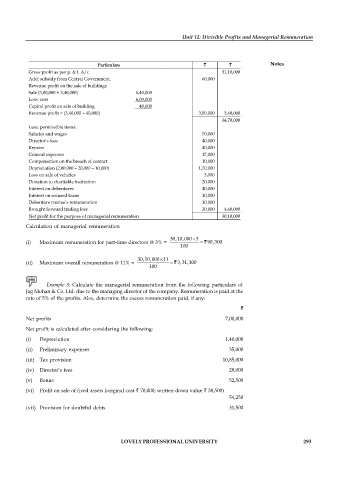
Particulars Notes
Gross profit as per p. & l. A/c 31,10,000
Add: subsidy from Central Government. 60,000
Revenue profit on the sale of buildings
Sale (3,00,000 + 3,40,000) 6,40,000
Less: cost 6,00,000
Capital profit on sale of building 40,000
Revenue profit = (3,40,000 – 40,000) 3,00,000 3,60,000
34,70,000
Less: permissible items:
Salaries and wages 70,000
Director’s fees 40,000
Repairs 40,000
General expenses 17,000
Compensation on the breach of contact 10,000
Depreciation (2,00,000 – 20,000 – 10,000) 1,70,000
Loss on sale of vehicles 3,000
Donation to charitable institution 20,000
Interest on debentures 40,000
Interest on secured loans 10,000
Debenture trustee’s remuneration 10,000
Brought forward trading loss 30,000 4,60,000
Net profit for the purpose of managerial remuneration 30,10,000
Calculation of managerial remuneration
30,10,000 3
(i) Maximum remuneration for part-time directors @ 3% = 90,300
100
30,10,000 11
(ii) Maximum overall remuneration @ 11% = 3,31,100
100
Example 3: Calculate the managerial remuneration from the following particulars of
Jag Mohan & Co. Ltd. due to the managing director of the company. Remuneration is paid at the
rate of 5% of the profits. Also, determine the excess remuneration paid, if any:
Net profits 7,00,000
Net profit is calculated after considering the following:
(i) Depreciation 1,40,000
(ii) Preliminary expenses 35,000
(iii) Tax provision 10,85,000
(iv) Director’s fees 28,000
(v) Bonus 52,500
(vi) Profit on sale of fixed assets (original cost 70,000; written down value 38,500)
54,250
(vii) Provision for doubtful debts 31,500
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 293