Page 125 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 125
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
Logic High Output Current, Ioh mA This is the maximum amount of current
that an output of a CMOS digital IC can
source while at Logic “1”.
Example of an Actual Spec:
–0.5 mA max. when Vss = 5V; Vin = 3.5V
Logic Low Output Current, Iol mA This is the maximum amount of current
that an output of a CMOS digital IC can
sink while at Logic “0”.
Example of an Actual Spec: +0.4 mA max.
when Vss = 5V; Vin = 1.5V
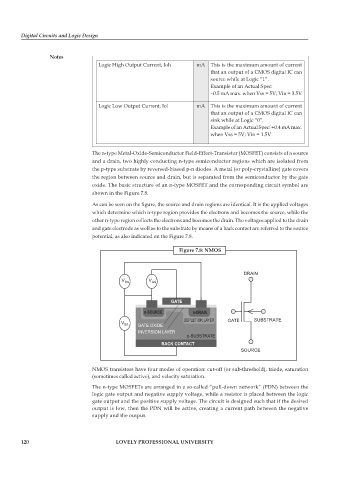
The n-type Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect-Transistor (MOSFET) consists of a source
and a drain, two highly conducting n-type semiconductor regions which are isolated from
the p-type substrate by reversed-biased p-n diodes. A metal (or poly-crystalline) gate covers
the region between source and drain, but is separated from the semiconductor by the gate
oxide. The basic structure of an n-type MOSFET and the corresponding circuit symbol are
shown in the Figure 7.8.
As can be seen on the figure, the source and drain regions are identical. It is the applied voltages
which determine which n-type region provides the electrons and becomes the source, while the
other n-type region collects the electrons and becomes the drain. The voltages applied to the drain
and gate electrode as well as to the substrate by means of a back contact are referred to the source
potential, as also indicated on the Figure 7.8.
Figure 7.8: NMOS
DRAIN
V V
DS GS
GATE
n-SOURCE n-DRAIN
DEPLETION LAYER GATE SUBSTRATE
V BS GATE OXIDE
INVERSION LAYER
p-SUBSTRATE
BACK CONTACT
SOURCE
NMOS transistors have four modes of operation: cut-off (or sub-threshold), triode, saturation
(sometimes called active), and velocity saturation.
The n-type MOSFETs are arranged in a so-called “pull-down network” (PDN) between the
logic gate output and negative supply voltage, while a resistor is placed between the logic
gate output and the positive supply voltage. The circuit is designed such that if the desired
output is low, then the PDN will be active, creating a current path between the negative
supply and the output.
120 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY