Page 121 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 121
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes method is so precise, it does not require masking—it just points and shoots the dopant
where it is needed. However, it is much slower than the atomic diffusion process.
Making Successive Layers
• The process of masking and etching or doping is repeated for each successive layer
depending on the doping process used until all of the integrated circuit chips are complete.
Sometimes a layer of silicon dioxide is laid down to provide an insulator between layers
or components. This is done through a process known as chemical vapour deposition, in
which the wafer’s surface is heated to about 752°F (400°C), and a reaction between the gases
silane and oxygen deposits a layer of silicon dioxide. A final silicon dioxide layer seals the
surface, a final etching opens up contact points, and a layer of aluminum is deposited to
make the contact pads. At this point, the individual ICs are tested for electrical function.
Making Individual ICs
• The thin wafer is like a piece of glass. The hundreds of individual chips are separated by
scoring a crosshatch of lines with a fine diamond cutter and then putting the wafer under
stress to cause each chip to separate. Those ICs that failed the electrical test are discarded.
Inspection under a microscope reveals other ICs that were damaged by the separation
process, and these are also discarded.
• The good ICs are individually bonded into their mounting package and the thin wire leads
are connected by either ultrasonic bonding or thermo compression. The mounting package
is marked with identifying part numbers and other information.
• The completed integrated circuits are sealed in anti-static plastic bags to be stored or shipped
to the end-user.
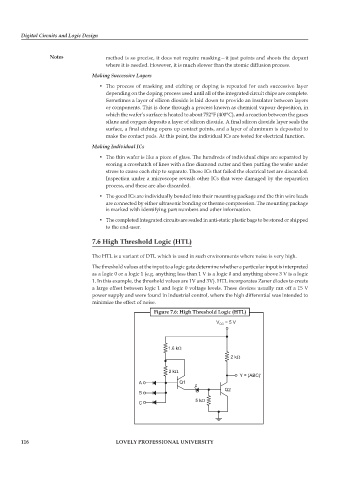
7.6 High Threshold Logic (HTL)
The HTL is a variant of DTL which is used in such environments where noise is very high.
The threshold values at the input to a logic gate determine whether a particular input is interpreted
as a logic 0 or a logic 1 (e.g. anything less than 1 V is a logic 0 and anything above 3 V is a logic
1. In this example, the threshold values are 1V and 3V). HTL incorporates Zener diodes to create
a large offset between logic 1 and logic 0 voltage levels. These devices usually ran off a 15 V
power supply and were found in industrial control, where the high differential was intended to
minimize the effect of noise.
Figure 7.6: High Threshold Logic (HTL)
V CC =5V
1.6 k
2k
2k
Y= (ABC)
A Q1
z
Q2
B
5k
C
116 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY