Page 254 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 254
Operations Management
Notes
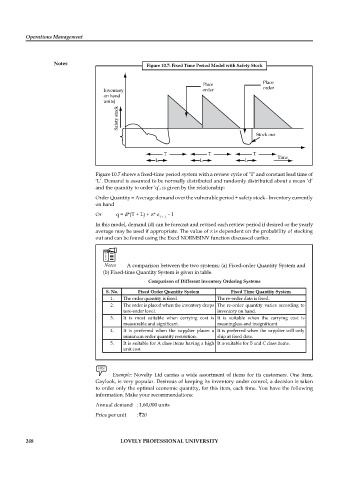
Figure 10.7: Fixed Time Period Model with Safety Stock
Figure 10.7 shows a fixed-time period system with a review cycle of ‘T’ and constant lead time of
‘L’. Demand is assumed to be normally distributed and randomly distributed about a mean ‘d’
and the quantity to order ‘q’, is given by the relationship:
Order Quantity = Average demand over the vulnerable period + safety stock - Inventory currently
on hand
Or q = d*(T + L) + z* σ – I
T + L
In this model, demand (d) can be forecast and revised each review period if desired or the yearly
average may be used if appropriate. The value of z is dependent on the probability of stocking
out and can be found using the Excel NORMSINV function discussed earlier.
A comparison between the two systems; (a) Fixed-order Quantity System and
(b) Fixed-time Quantity System is given in table.
Comparison of Different Inventory Ordering Systems
S. No. Fixed Order Quantity System Fixed Time Quantity System
1. The order quantity is fixed The re-order data is fixed.
2. The order is placed when the inventory drops The re-order quantity varies according to
tore-order level. inventory on hand.
3. It is most suitable when carrying cost is It is suitable when the carrying cost is
measurable and significant. meaningless and insignificant
4. It is preferred when the supplier places a It is preferred when the supplier will only
minimum order quantity restriction. ship at fixed date.
5. It is suitable for A class items having a high It is suitable for B and C class items.
unit cost
Example: Novelty Ltd carries a wide assortment of items for its customers. One item,
Gaylook, is very popular. Desirous of keeping its inventory under control, a decision is taken
to order only the optimal economic quantity, for this item, each time. You have the following
information. Make your recommendations:
Annual demand : 1,60,000 units
Price per unit : 20
248 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY