Page 255 - DMGT501_OPERATIONS_MANAGEMENT
P. 255
Unit 10: Economic Order Quantity
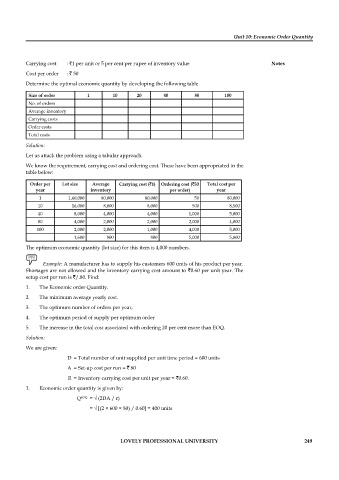
Carrying cost : 1 per unit or 5 per cent per rupee of inventory value Notes
Cost per order : 50
Determine the optimal economic quantity by developing the following table
Size of order 1 10 20 40 80 100
No. of orders
Average inventory
Carrying costs
Order costs
Total costs
Solution:
Let us attack the problem using a tabular approach.
We know the requirement, carrying cost and ordering cost. These have been appropriated in the
table below:
Order per Lot size Average Carrying cost ( 1) Ordering cost ( 50 Total cost per
year inventory per order) year
1 1,60,000 80,000 80,000 50 80,000
10 16,000 8,000 8,000 500 8,500
40 8,000 4,000 4,000 1,000 5,000
80 4,000 2,000 2,000 2,000 4,000
100 2,000 2,000 1,000 4,000 5,000
1,600 800 800 5,000 5,800
The optimum economic quantity (lot size) for this item is 4,000 numbers.
Example: A manufacturer has to supply his customers 600 units of his product per year.
Shortages are not allowed and the inventory carrying cost amount to 0.60 per unit year. The
setup cost per run is /.80. Find:
1. The Economic order Quantity.
2. The minimum average yearly cost.
3. The optimum number of orders per year,
4. The optimum period of supply per optimum order
5. The increase in the total cost associated with ordering 20 per cent more than EOQ.
Solution:
We are given:
D = Total number of unit supplied per unit time period = 600 units
A = Set-up cost per run = 80
R = Inventory carrying cost per unit per year = 0.60.
1. Economic order quantity is given by:
Q EOQ = √ (2DA / r)
= √ [(2 × 600 × 80) / 0.60] = 400 units
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 249