Page 115 - DMGT518_TRAINING_AND_DEVELOPMENT_SYSTEM
P. 115
Training and Development System
Notes
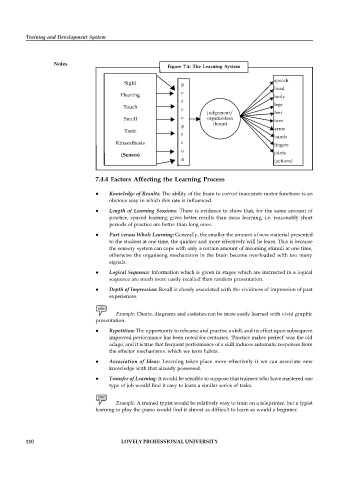
Figure 7.4: The Learning System
speech
Sight p
head
e
Hearing body
r
Touch legs
c
judgement/ feet
Smell e organisation toes
(brain)
p
Taste arms
t
hands
Kinaesthesis i
fingers
o joints
(Senses)
n (actions)
7.4.4 Factors Affecting the Learning Process
Knowledge of Results: The ability of the brain to correct inaccurate motor functions is an
obvious way in which this rate is influenced.
Length of Learning Sessions: There is evidence to show that, for the same amount of
practice, spaced learning gives better results than mass learning, i.e. reasonably short
periods of practice are better than long ones.
Part versus Whole Learning: Generally, the smaller the amount of new material presented
to the student at one time, the quicker and more effectively will he learn. This is because
the sensory system can cope with only a certain amount of incoming stimuli at one time,
otherwise the organising mechanisms in the brain become overloaded with too many
signals.
Logical Sequence: Information which is given in stages which are instructed in a logical
sequence are much more easily recalled than random presentation.
Depth of Impression: Recall is closely associated with the vividness of impression of past
experiences.
Example: Charts, diagrams and statistics can be more easily learned with vivid graphic
presentation.
Repetition: The opportunity to rehearse and practise a skill, and its effect upon subsequent
improved performance has been noted for centuries. ‘Practice makes perfect’ was the old
adage, and it is true that frequent performance of a skill induces automatic responses from
the effector mechanisms, which we term habits.
Association of Ideas: Learning takes place more effectively if we can associate new
knowledge with that already possessed.
Transfer of Learning: It would be sensible to suppose that trainees who have mastered one
type of job would find it easy to learn a similar series of tasks.
Example: A trained typist would be relatively easy to train on a teleprinter, but a typist
learning to play the piano would find it almost as difficult to learn as would a beginner.
110 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY