Page 44 - DMGT518_TRAINING_AND_DEVELOPMENT_SYSTEM
P. 44
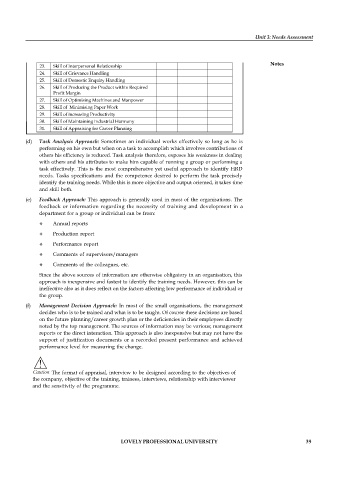
Name of Appraiser .......................................... Dept .............................................................................
of ............................................................................................................. ...................................................
Nice to
Subject Knowledge
Must
know
required
know
1.
Role of a Technician
2.
3.
Role of an Inspector
Role of an Instructor
4.
5.
Role of a Worker or Subordinate
6.
Knowledge of Budgeting and Planning
Knowledge of Monitoring and Controlling
7.
8.
Knowledge of Discipline
Knowledge of Conducting Meeting
9.
10.
Knowledge of Delivering a Talk
Knowledge of Appraising the Work
11.
12.
Knowledge of Trade Union Working
Knowledge of Labour Laws
13.
Knowledge of Quality Concepts
14. Role of a Supervisor Not
15. Knowledge of Safety Measures
16. Knowledge of Methods of improvement
17. Knowledge of Routine Working
18. Knowledge of Value Analysis
19. Knowledge of Cost Effectiveness Unit 3: Needs Assessment
20. Skill of leadership
21. Skill of Effective Communication
22. Skill of Decision-Making
Notes
23. Skill of Interpersonal Relationship
24. Skill of Grievance Handling
25. Skill of Domestic Enquiry Handling
26. Skill of Producing the Product within Required
Profit Margin
27. Skill of Optimising Machines and Manpower
28. Skill of Minimising Paper Work
29. Skill of increasing Productivity
30. Skill of Maintaining industrial Harmony
31. Skill of Appraising for Career Planning
(d) Task Analysis Approach: Sometimes an individual works effectively so long as he is
performing on his own but when on a task to accomplish which involves contributions of
others his efficiency is reduced. Task analysis therefore, exposes his weakness in dealing
with others and his attributes to make him capable of running a group or performing a
task effectively. This is the most comprehensive yet useful approach to identify HRD
needs. Tasks specifications and the competence desired to perform the task precisely
identify the training needs. While this is more objective and output oriented, it takes time
and skill both.
(e) Feedback Approach: This approach is generally used in most of the organisations. The
feedback or information regarding the necessity of training and development in a
department for a group or individual can be from:
Annual reports
Production report
Performance report
Comments of supervisors/managers
Comments of the colleagues, etc.
Since the above sources of information are otherwise obligatory in an organisation, this
approach is inexpensive and fastest to identify the training needs. However, this can be
ineffective also as it does reflect on the factors affecting low performance of individual or
the group.
(f) Management Decision Approach: In most of the small organisations, the management
decides who is to be trained and what is to be taught. Of course these decisions are based
on the future planning/career growth plan or the deficiencies in their employees directly
noted by the top management. The sources of information may be various; management
reports or the direct interaction. This approach is also inexpensive but may not have the
support of justification documents or a recorded present performance and achieved
performance level for measuring the change.
!
Caution The format of appraisal, interview to be designed according to the objectives of
the company, objective of the training, trainees, interviews, relationship with interviewer
and the sensitivity of the programme.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 39