Page 254 - DCOM205_ACCOUNTING_FOR_COMPANIES_II
P. 254
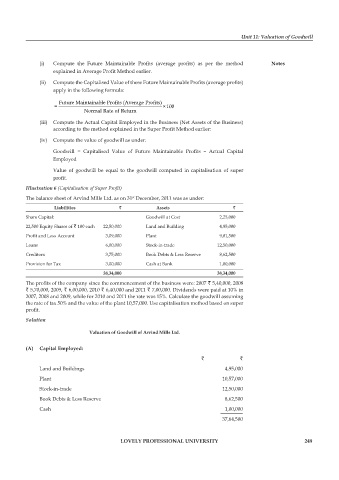
Unit 11: Valuation of Goodwill
(i) Compute the Future Maintainable Profits (average profits) as per the method notes
explained in Average Profit Method earlier.
(ii) Compute the Capitalised Value of these Future Maintainable Profits (average profits)
apply in the following formula:
Future Maintainable Profits (Average Profits)
= ×100
Normal Rate of Return
(iii) Compute the Actual Capital Employed in the Business (Net Assets of the Business)
according to the method explained in the Super Profit Method earlier:
(iv) Compute the value of goodwill as under:
Goodwill = Capitalised Value of Future Maintainable Profits – Actual Capital
Employed
Value of goodwill be equal to the goodwill computed in capitalisation of super
profit.
Illustration 6 (Capitalisation of Super Profit)
The balance sheet of Arvind Mills Ltd. as on 31 December, 2011 was as under:
st
liabilities ` assets `
Share Capital: Goodwill at Cost 2,25,000
22,500 Equity Shares of ` 100 each 22,50,000 Land and Building 4,95,000
Profit and Loss Account 3,09,000 Plant 9,01,500
Loans 6,00,000 Stock-in-trade 12,50,000
Creditors 3,75,000 Book Debts & Less Reserve 8,62,500
Provision for Tax 3,00,000 Cash at Bank 1,00,000
38,34,000 38,34,000
The profits of the company since the commencement of the business were: 2007 ` 5,40,000, 2008
` 5,70,000, 2009, ` 6,00,000, 2010 ` 6,40,000 and 2011 ` 7,00,000. Dividends were paid at 10% in
2007, 2008 and 2009, while for 2010 and 2011 the rate was 15%. Calculate the goodwill assuming
the rate of tax 50% and the value of the plant 10,57,000. Use capitalisation method based on super
profit.
Solution
valuation of goodwill of arvind mills ltd.
(a) capital employed:
` `
Land and Buildings 4,95,000
Plant 10,57,000
Stock-in-trade 12,50,000
Book Debts & Less Reserve 8,62,500
Cash 1,00,000
37,64,500
lovely professional university 249