Page 161 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 161
Digital Circuits and Logic Design
Notes
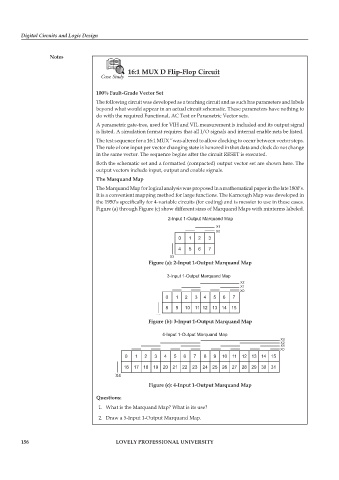
16:1 MUX D Flip-Flop Circuit
100% Fault-Grade Vector Set
The following circuit was developed as a teaching circuit and as such has parameters and labels
beyond what would appear in an actual circuit schematic. These parameters have nothing to
do with the required Functional, AC Test or Parametric Vector sets.
A parametric gate-tree, used for VIH and VIL measurement is included and its output signal
is listed. A simulation format requires that all I/O signals and internal enable nets be listed.
The test sequence for a 16:1 MUX ‘’was altered to allow clocking to occur between vector steps.
The rule of one input per vector changing state is honored in that data and clock do not change
in the same vector. The sequence begins after the circuit RESET is executed.
Both the schematic set and a formatted (compacted) output vector set are shown here. The
output vectors include input, output and enable signals.
The Marquand Map
The Marquand Map for logical analysis was proposed in a mathematical paper in the late 1800’s.
It is a convenient mapping method for large functions. The Karnough Map was developed in
the 1950’s specifically for 4-variable circuits (for coding) and is messier to use in these cases.
Figure (a) through Figure (c) show different sizes of Marquand Maps with minterms labeled.
Figure (a): 2-Input 1-Output Marquand Map
Figure (b): 3-Input 1-Output Marquand Map
Figure (c): 4-Input 1-Output Marquand Map
Questions:
1. What is the Marquand Map? What is its use?
2. Draw a 5-Input 1-Output Marquand Map.
156 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY