Page 200 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 200
Unit 11: Registers and Counters
Notes
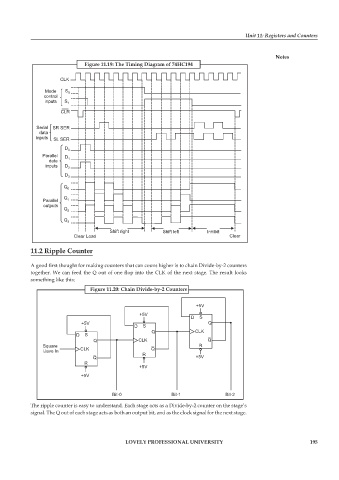
Figure 11.19: The Timing Diagram of 74HC194
CLK
Mode S 0
control
inputs S 1
CLR
Serial SR SER
data
inputs SL SER
D 0
Parallel D
data 1
inputs D 2
D
3
Q
0
Q
Parallel 1
outputs
Q 2
Q 3
Shift right Shift left Inhibit
Clear Load Clear
11.2 Ripple Counter
A good first thought for making counters that can count higher is to chain Divide-by-2 counters
together. We can feed the Q out of one flop into the CLK of the next stage. The result looks
something like this:
Figure 11.20: Chain Divide-by-2 Counters
+5V
+5V
D S
+5V Q
D S
Q CLK
D S
Q CLK Q
Square R
iJave In CLK Q
R
Q +5V
R
+5V
+5V
Bit-0 Bit-1 Bit-2
The ripple counter is easy to understand. Each stage acts as a Divide-by-2 counter on the stage’s
signal. The Q out of each stage acts as both an output bit, and as the clock signal for the next stage.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 195