Page 204 - DCAP108_DIGITAL_CIRCUITS_AND_LOGIC_DESIGNS
P. 204
Unit 11: Registers and Counters
There are many variations to the basic binary counter. The one described above is the binary up Notes
counter (counts upwards). Besides the up counter, there is the binary down counter, the binary
up/down counter, binary-coded-decimal (BCD) counter, etc. Any counter that counts in binary
is called a binary counter.
11.3.2 Binary Down Counters
In a binary up counter, a particular bit, except for the first bit, toggles if all the lower-order bits
are 1’s. The opposite is true for binary down counters. That is, a particular bit toggles if all the
lower-order bits are 0’s and the first bit toggles on every pulse.
Taking an example, A A A A = 0100. On the next count, A A A A = 0011. A , the lowest-
1
4
2
3
1
3
4
1
2
order bit, is always complemented. A is complemented because all the lower-order positions
2
(A only in this case) are 0’s. A is also complemented because all the lower-order positions, A
1
3
2
and A are 0’s. But A is not complemented the lower-order positions, A A A = 011, do not give
3
4
1
2
1
an all 0 condition.
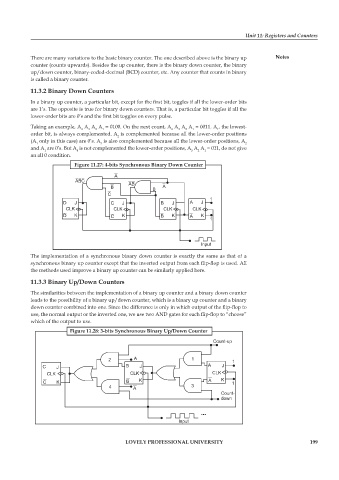
Figure 11.27: 4-bits Synchronous Binary Down Counter
The implementation of a synchronous binary down counter is exactly the same as that of a
synchronous binary up counter except that the inverted output from each flip-flop is used. All
the methods used improve a binary up counter can be similarly applied here.
11.3.3 Binary Up/Down Counters
The similarities between the implementation of a binary up counter and a binary down counter
leads to the possibility of a binary up/down counter, which is a binary up counter and a binary
down counter combined into one. Since the difference is only in which output of the flip-flop to
use, the normal output or the inverted one, we use two AND gates for each flip-flop to “choose”
which of the output to use.
Figure 11.28: 3-bits Synchronous Binary Up/Down Counter
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 199